History
 One of many issues we techniques consultants are sometimes asked is Who came up with this within the first place?” That is indeed of robust query to answer. For these of us who’re deeply entrenched within the information age, there are numerous technical breakthroughs we are able to point to, however there is one invention that actually started it all.
One of many issues we techniques consultants are sometimes asked is Who came up with this within the first place?” That is indeed of robust query to answer. For these of us who’re deeply entrenched within the information age, there are numerous technical breakthroughs we are able to point to, however there is one invention that actually started it all.
teleprinterFlominator For many years teleprinters used the five-bit Baudot Code and, in some cases, other specialized codes. With the appearance of computer systems , however, it became obvious that the Baudot Code was now not ample, and in 1966 the American Normal Code for Info Interchange ( ASCII ) was established. ASCII consisted of seven bits, compared with 5 bits for the Baudot Code; these allowed 128 totally different coded letters or symbols, as compared with 32 for the Baudot Code. Code speeds of one hundred fifty words per minute … Read the rest

 Telegraph key, telegraph history, Vibroplex, Vibroplex bug, key, sounder, relay, morse code, morse registers, railroad telegraph, telegraph sounder, name field, leg key, legless key.
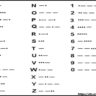
Telegraph key, telegraph history, Vibroplex, Vibroplex bug, key, sounder, relay, morse code, morse registers, railroad telegraph, telegraph sounder, name field, leg key, legless key. In 1832 Samuel F.B. Morse, a professor of portray and sculpture on the College of the City of New York (later New York University), became fascinated by the potential of electrical telegraphy and made sketches of ideas for such a system. In 1835 he devised a system of dots and dashes to signify letters and numbers. In 1837 he was granted a patent on an electromagnetic telegraph.
In 1832 Samuel F.B. Morse, a professor of portray and sculpture on the College of the City of New York (later New York University), became fascinated by the potential of electrical telegraphy and made sketches of ideas for such a system. In 1835 he devised a system of dots and dashes to signify letters and numbers. In 1837 he was granted a patent on an electromagnetic telegraph. Earlier than the development of the electric telegraph within the 19th century revolutionized how info was transmitted across long distances, historical civilizations corresponding to these in China, Egypt and Greece used drumbeats or smoke signals to exchange info between far-flung factors. Nevertheless, such methods were limited by the climate and the necessity for an uninterrupted line of sight between receptor factors. These limitations also lessened the effectiveness of the semaphore, a contemporary precursor to the electric telegraph. Developed within the early 1790s, the semaphore consisted of a sequence of hilltop stations that each had massive movable arms to signal letters and numbers and two telescopes with which to see the other stations. Like ancient smoke indicators, the semaphore was inclined to climate and other factors that hindered visibility. A special methodology of transmitting information was needed to make common and dependable long-distance communication workable.
Earlier than the development of the electric telegraph within the 19th century revolutionized how info was transmitted across long distances, historical civilizations corresponding to these in China, Egypt and Greece used drumbeats or smoke signals to exchange info between far-flung factors. Nevertheless, such methods were limited by the climate and the necessity for an uninterrupted line of sight between receptor factors. These limitations also lessened the effectiveness of the semaphore, a contemporary precursor to the electric telegraph. Developed within the early 1790s, the semaphore consisted of a sequence of hilltop stations that each had massive movable arms to signal letters and numbers and two telescopes with which to see the other stations. Like ancient smoke indicators, the semaphore was inclined to climate and other factors that hindered visibility. A special methodology of transmitting information was needed to make common and dependable long-distance communication workable. One of the vital innovations in the discipline of communications during the modern age is the telephone. It is because of this invention that we are in a position to talk to our associates and families without the trouble of traveling far and going to their place. But many people as of late have forgotten and never recognize the importance of phone in our lives.
One of the vital innovations in the discipline of communications during the modern age is the telephone. It is because of this invention that we are in a position to talk to our associates and families without the trouble of traveling far and going to their place. But many people as of late have forgotten and never recognize the importance of phone in our lives.